How to Fix Laptop Overheating Using BIOS Settings. Laptop Overheating is the most common issues faced by laptop users. It not only affects system performance but can also lead to permanent hardware damage if not addressed in time. While software solutions and cleaning dust buildup are common fixes, many users overlook BIOS-level configurations that directly impact thermal performance. In this article, we’ll show you how to fix laptop overheating using BIOS settings effectively and safely.
Why Use BIOS to Fix Overheating?
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI is a low-level system that controls essential hardware behavior before the operating system loads. BIOS settings allow you to access fan speed controls, thermal throttling options, and even disable CPU features like Turbo Boost that generate excess heat. Fixing laptop heating problems without software is possible by learning the right BIOS tweaks.
Understanding the Causes of Laptop Overheating:
Before jumping into BIOS adjustments, it’s helpful to understand why laptops overheat in the first place:
These issues can be alleviated by using BIOS fan control settings and adjusting thermal options from within the firmware.
How to Fix Laptop Overheating Using BIOS Settings:
Follow these steps to access BIOS and apply the correct settings to reduce overheating.
1.Enter BIOS or UEFI Mode:
To access BIOS settings:
1.Shut down your laptop completely.
2.Press the power button and immediately press the BIOS key (usually Del, F2, Esc, or F10, depending on your manufacturer).
3.You’ll enter the BIOS/UEFI interface.
Make sure to consult your laptop manual or manufacturer website if you’re unsure about your specific BIOS access key.
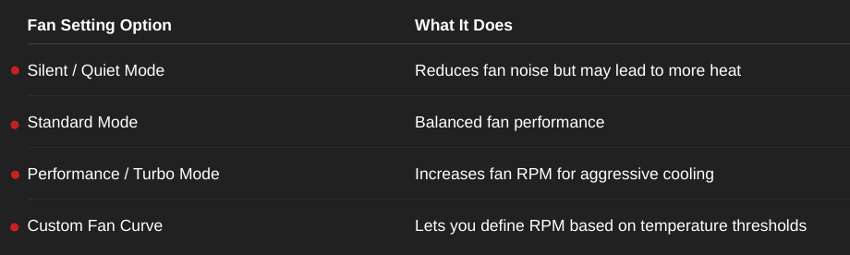
2.Change Fan Settings from BIOS:
Many modern laptops allow you to configure fan speed profiles directly from the BIOS.
If available, choose Performance Mode or custom fan curve to increase cooling. This helps with laptop thermal management and ensures active airflow under heavy load.
3.Adjust CPU Temperature Limit in BIOS:
Most BIOS interfaces have a CPU temperature limit setting. This allows you to throttle performance once the CPU reaches a specific temperature (usually between 80°C to 100°C).
Lower the maximum CPU temp threshold slightly (e.g., from 100°C to 85°C) to initiate earlier throttling.
This prevents thermal shutdown and reduces long-term hardware strain.
4.Disable Intel Turbo Boost (Optional):
If your laptop supports Intel Turbo Boost, disabling it can significantly lower heat generation.
Steps:
1.Navigate to Advanced > CPU Configuration.
2.Look for Intel Turbo Boost and set it to Disabled.
3.This will reduce CPU spikes and help reduce CPU overheating via BIOS.
5.Enable Advanced Thermal Options in BIOS:
Some BIOS versions have additional thermal features:
-Dynamic Thermal Framework (DTF)
-ACPI Thermal Management
-Passive Cooling vs Active Cooling
Set Active Cooling as default and enable any Intel/AMD thermal framework settings. This is part of BIOS settings for optimal cooling and can help greatly in maintaining temperature control.
6.Save and Exit BIOS:
Once you’ve made all the changes:
1.Press F10 or select “Save Changes and Exit.”
Your laptop will reboot with the new BIOS cooling settings active.
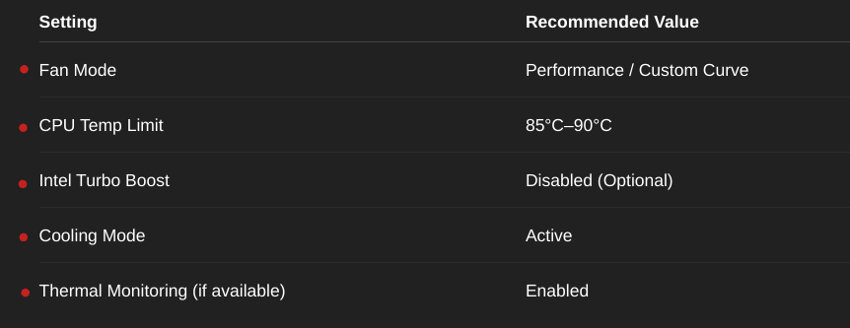
📋 Recommended BIOS Settings Summary
These are the best BIOS settings for laptop cooling that can be safely applied by users.
BIOS Tweaks for Windows 11 Users:
If you’re wondering how to fix laptop overheating using BIOS settings in Windows 11, the process is the same. Windows version doesn’t affect BIOS access, but after applying BIOS changes, ensure that Windows Power Mode is set to Balanced or Better Performance, not Best Performance, to avoid additional strain on the CPU.
Can BIOS Update Fix Overheating?
Yes, in some cases. Manufacturers often release BIOS updates that include better thermal management algorithms, fan profiles, and system stability fixes.
To update BIOS safely:
1.Visit your laptop manufacturer’s support page.
2.Search for the latest BIOS firmware.
3.Follow official instructions carefully.
4.This acts as a laptop overheating issue fix from the root level.
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1.Can I fix overheating without software tools?
Yes. You can fix laptop heating problems without software by tweaking BIOS settings like fan speed, CPU limits, and disabling Turbo Boost.
Q2.Is it safe to change fan settings from BIOS?
Yes, as long as you don’t disable fans or set them to run below recommended RPM. BIOS fan control settings are safe and designed for thermal customization.
Q3.What if my BIOS doesn’t have thermal settings?
Some laptops (especially entry-level ones) have locked BIOS. In such cases, use software tools like HWMonitor or contact the manufacturer for a BIOS update.
Q4.Does undervolting help reduce overheating?
Yes, undervolting reduces power to the CPU, which lowers heat. Some BIOS versions allow undervolting directly, but many now restrict this due to stability concerns.
📝 Final Thoughts:
Knowing how to fix laptop overheating using BIOS settings gives you direct control over your hardware’s cooling behavior. By making adjustments such as increasing fan speeds, lowering CPU thermal limits, and disabling Turbo Boost, you can significantly extend the life of your laptop and maintain optimal performance. Always make BIOS changes cautiously, and if in doubt, consult your laptop’s support documentation.