Password Managers vs Browser Passwords – A Complete Security Comparison. Managing dozens of logins has become a daily challenge in today’s digital world. From social media accounts to banking apps and SaaS platforms, users rely heavily on saved credentials for convenience. This has sparked a major debate: Password Managers vs Browser Passwords — which option truly protects your online identity?
While browser-based password saving feels effortless, dedicated password managers promise advanced protection like encrypted password storage, password vault protection, and zero-knowledge encryption. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore how both systems work, compare their security models, uncover real-world risks, and help you decide the safest option for long-term online account security.

How Do Browser Passwords Work?
Most modern browsers like Chrome, Edge, and Firefox include a built-in password-saving feature. When you log in to a website, the browser prompts you to store your credentials locally or sync them across devices.
Understanding how do browser passwords work is essential before trusting them. Browser credentials are typically stored in a local database, sometimes synced through your browser account. While browsers claim encryption, browser password manager security is tightly tied to the device’s login and overall system security.
However, this convenience comes with hidden vulnerabilities, especially when attackers gain access to your browser profile or exploit autofill password security risks.
Risks of Browser Saved Passwords
Although popular, there are serious risks of browser saved passwords that many users overlook:
- Malware can extract stored credentials
- Anyone with system access can view passwords
- Limited protection against phishing attacks
- Weak control over local vs cloud password storage
The risks of saving passwords in browsers increase significantly on shared or compromised devices, making them a common target for cybercriminals.
Browser Password Storage – Strengths & Weaknesses
| Feature | Browser Password Manager |
|---|---|
| Encryption | Basic encryption tied to OS |
| 2FA Protection | ❌ Limited |
| Cross-Device Sync | ✅ Browser account dependent |
| Password Vault | ❌ No dedicated vault |
| Attack Resistance | ⚠️ Moderate to low |
How Password Managers Work?
Dedicated tools take a completely different approach. Understanding how password managers work explains why they are considered safer.
A dedicated password manager software creates a secure vault protected by a master password. All credentials are stored using encrypted password storage, often secured by zero-knowledge encryption, meaning even the provider cannot access your data.
Most cloud-based password managers also offer offline access, device syncing, and emergency recovery options, dramatically improving password manager security.
Benefits of Password Managers
The growing popularity of password managers is driven by their strong security and advanced features. The benefits of password managers go far beyond simple storage:
- Centralized password vault protection
- Built-in password generators
- Two-factor authentication support
- Strong phishing and breach protection
- Secure sharing for teams and families
These features significantly improve online account security, especially for users managing dozens of logins daily.
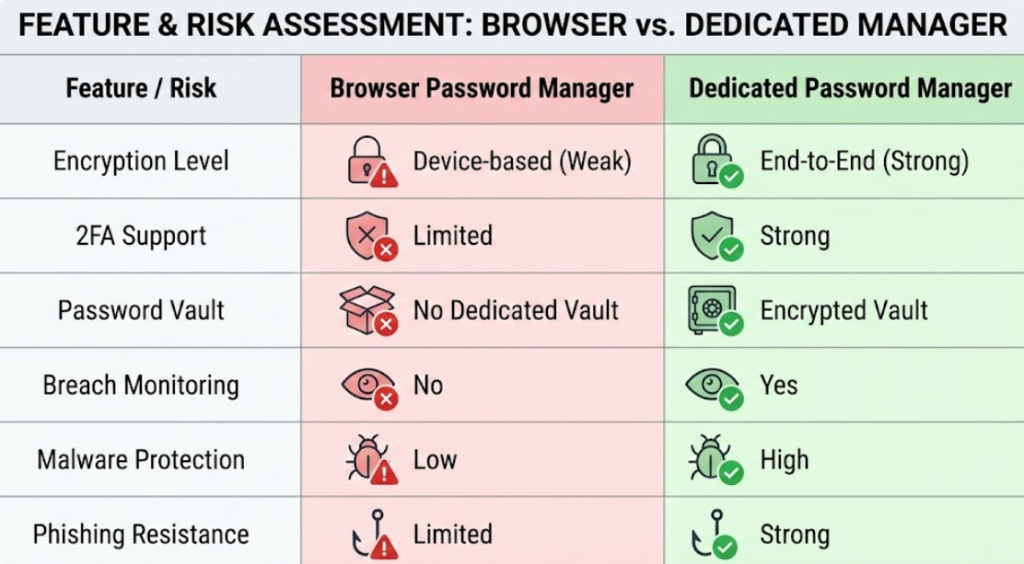
Password Managers vs Browser Passwords: Core Security Differences
This is where the real comparison begins. Password Managers vs Browser Passwords is not just about convenience—it’s about how each system defends against modern cyber threats.
Password Manager vs Browser Password Manager Security
| Security Aspect | Browser Password Manager | Dedicated Password Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption Level | Device-based | End-to-end encryption |
| Zero-Knowledge Model | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| 2FA Support | ❌ Limited | ✅ Strong |
| Breach Monitoring | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Password Vault | ❌ No | ✅ Encrypted vault |
When comparing password managers vs browser saved passwords, the difference in protection layers becomes immediately clear.
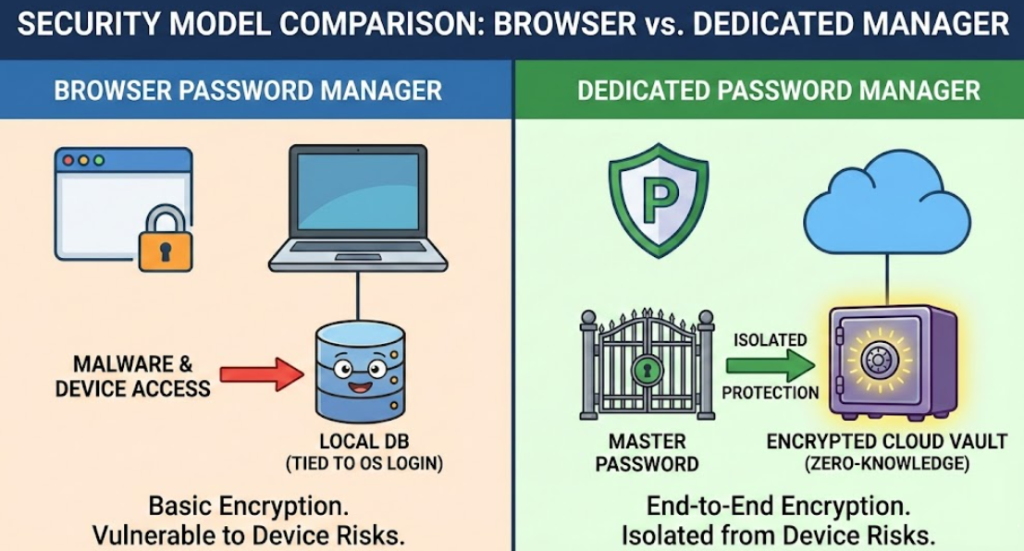
Are Password Managers Safer Than Browsers?
A common question users ask is: Are password managers safer than browsers? The short answer is yes—by a significant margin.
Browsers prioritize usability, not advanced credential protection. Dedicated password managers, on the other hand, are built exclusively for securing sensitive data. They mitigate autofill password security risks, defend against keylogging, and isolate passwords from browser-based exploits.
From a cybersecurity standpoint, a browser password manager vs password manager comparison clearly favors specialized tools.
Local vs Cloud Password Storage Explained
One major concern users have involves local vs cloud password storage. While browser passwords often rely on local storage synced through browser accounts, password managers use secure cloud vaults protected by strong cryptography.
Contrary to myths, cloud-based password managers are often safer than local browser storage due to continuous security audits, breach detection, and multi-layer authentication.
Local vs Cloud Password Storage Comparison
| Storage Type | Security Level | Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Local Browser Storage | Low–Medium | Device theft, malware |
| Synced Browser Storage | Medium | Account compromise |
| Cloud Password Manager | High | Strong encryption, 2FA |
Password Managers vs Browser Passwords – Pros, Cons, and Security Risks
Let’s summarize the real-world tradeoffs of Password Managers vs Browser Passwords – Pros, Cons, and Security Risks:
Browser Password Managers
✔ Easy to use
✔ No extra software
❌ Weak security model
❌ High exposure to malware
Dedicated Password Managers
✔ Advanced password manager security
✔ Strong encryption and vault isolation
✔ Protection against phishing and breaches
❌ Requires setup and learning curve
For anyone serious about protecting digital identities, Password Managers vs Browser Passwords is no longer a close contest.
Which Option Should You Choose?
If you value convenience over security, browser password managers may suffice for low-risk accounts. However, for banking, work platforms, crypto wallets, or SaaS tools, relying on browsers exposes you to unnecessary risks.
A dedicated password manager software provides long-term safety, scalability, and peace of mind, especially as cyber threats continue to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are browser password managers safe for banking?
No. Due to limited encryption and lack of vault isolation, browser passwords are not recommended for financial accounts.
2. Do password managers store passwords in the cloud?
Yes, but they use zero-knowledge encryption, ensuring only you can access your data.
3. Can password managers be hacked?
While no system is 100% immune, dedicated password managers significantly reduce attack surfaces compared to browsers.
4. Should I delete saved browser passwords?
If you switch to a password manager, deleting browser-saved passwords is highly recommended to reduce exposure.
Final Verdict
When evaluating Password Managers vs Browser Passwords, the conclusion is clear: browser tools offer convenience, but password managers deliver true security. With encrypted vaults, two-factor authentication, and advanced breach protection, password managers are the smarter choice for safeguarding modern digital lives.